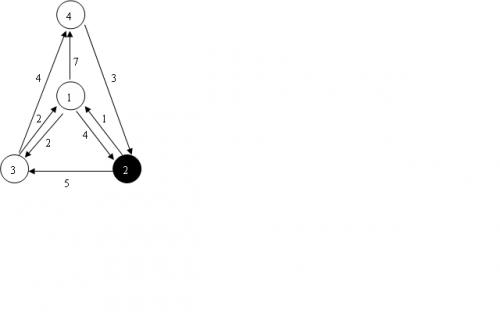
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
| #include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cctype>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1000 + 10;
const int MAXM = 100000 + 10;
struct Edge {
int prev;
int next;
int weight;
} edge[MAXM], edgeReversed[MAXM];
int n, m, x, cnt, maxWeight = -1;
int dis[MAXN], head[MAXN], disReversed[MAXN], headReversed[MAXN];
bool inQueue[MAXN], inQueueReversed[MAXN];
inline int getint() {
int s = 0, x = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while (!isdigit(ch)) {
(ch == '-') && (x = -1);
ch = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(ch)) {
s = s * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return s * x;
}
inline void addEdgeReversed(int prev, int next, int weight) {
edgeReversed[cnt].prev = prev;
edgeReversed[cnt].weight = weight;
edgeReversed[cnt].next = headReversed[next];
headReversed[next] = cnt;
}
inline void addEdge(int prev, int next, int weight) {
edge[++cnt].prev = prev;
edge[cnt].weight = weight;
edge[cnt].next = head[next];
head[next] = cnt;
addEdgeReversed(next, prev, weight);
}
inline void Dijkstra(int s, int n) {
memset(inQueue, 0, sizeof(inQueue));
for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) dis[i] = 2147483647;
std::priority_queue<std::pair<int, int>, std::vector<std::pair<int, int> >, std::greater<std::pair<int, int> > > q;
inQueue[s] = true;
q.push(make_pair(s, 0));
dis[s] = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int prev = q.top().first;
int weight = q.top().second;
q.pop();
inQueue[prev] = false;
for (int e = head[prev]; e; e = edge[e].next) {
if (dis[edge[e].prev] > edge[e].weight + weight) {
dis[edge[e].prev] = edge[e].weight + weight;
q.push(make_pair(edge[e].prev, dis[edge[e].prev]));
}
}
}
}
inline void DijkstraReversed(int s, int n) {
memset(inQueueReversed, 0, sizeof(inQueueReversed));
for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) disReversed[i] = 2147483647;
std::priority_queue<std::pair<int, int>, std::vector<std::pair<int, int> >, std::greater<std::pair<int, int> > > q;
inQueueReversed[s] = true;
q.push(make_pair(s, 0));
while (!q.empty()) {
int prev = q.top().first;
int weight = q.top().second;
q.pop();
inQueueReversed[prev] = false;
for (int e = headReversed[prev]; e; e = edgeReversed[e].next) {
if (disReversed[edgeReversed[e].prev] > edgeReversed[e].weight + weight) {
disReversed[edgeReversed[e].prev] = edgeReversed[e].weight + weight;
q.push(make_pair(edgeReversed[e].prev, disReversed[edgeReversed[e].prev]));
}
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char *const argv[]) {
n = getint(), m = getint(), x = getint();
int tm = m;
while (tm --> 0) {
int prev = getint(), next = getint(), weight = getint();
addEdge(prev, next, weight);
}
int tn = n;
Dijkstra(x, n);
DijkstraReversed(x, n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
maxWeight = std::max(maxWeight, dis[i] + disReversed[i]);
}
printf("%d\n", maxWeight);
return 0;
}
|